People look upon Australia as the home of every dangerous creature that walks, crawls, or throws telephones at hotel staff. This is true. But anyone with Australian friends – and not just those people you have webcam sex with – will tell you that Aussies seem to survive in spite of all this death.
Like every country, a lot of attention is focused on the stuff that doesn’t actually kill us that much (spiders) rather than stuff that kills most people (being a round, gelatinous ball of lard). So here are the 10 most deadly animals in Australia for 2000-2010 according to the National Coroners Information System of Australia.
10) Emus
Right now you are probably wondering what an emu is and why it killed 5 people. The easiest way to describe the emu is as an Australian version of the ostrich; that is, a long legged, long necked, flightless bird, and being Australian it is likely to be wearing a hat with corks dangling from it. And it’s planning to kill you.
Five people isn’t a huge death toll for an Australian animal, but you have to remember that emus like to live in the middle of the country. You know, the part of Australia that people avoid because it is too hot and lacks beaches. So emus only occasionally have the opportunity to kill people.
They also won a war against Aussie soldiers. Because machineguns mean nothing to emus – partly because they are birds and don’t understand guns, and partly because they are immune to them.
9) Crocodiles
If there is a muddy river in Australia there is a good chance there is a crocodile waiting to eat someone in it. Unfortunately for the crocodiles, Aussies and tourists have gotten wise to their antics after watching Crocodile Dundee and they have only been able to snack on 9 people.
Since people are more aware of crocodiles, they now act as sign enforcement officers. Most rivers and water holes have warning signs that tell people not to go swimming on penalty of death. Crocs are there to make sure those signs are enforced.
8) Snakes
Racking up a measly 14 deaths for the decade are venomous snakes. That’s right; Australia is home to pretty much all of the most deadly snakes in the world and they only manage to kill 1.4 people a year.
Australian snakes make all other country’s snakes look as pathetic as a 50 year old at a nightclub trying to hit on a group of teens. In other countries snakebite is treated as a painful experience that might require a hospital visit. Might. In the next day or two. In Australia a snakebite is pretty much a death sentence, with snakes ranked in terms of how many minutes you have to get antivenin into your body before you’ll be visiting the morgue.
So why the low death count? Why is one of the most feared animals in a country filled with deadly animals killing so few people?
Well, when you live in a country like Australia with so many poisonous critters trying to kill you, the local hospitals, and people who are scared of their own shadows, like to stock up on antivenins. Ambulances are used to bringing some antivenin to you. So the reason snakes don’t kill that many people is down to the way Aussies deal with snakebites.
Take the recent example of an average Aussie bloke. The world’s second most deadly snake bites him and he does two things: calls an ambulance and grabs a nice cold beer. Because if you’re going to die, you might as well die refreshed. After dispatching the snake that bit him, the man was cool, calm and collected. If the ambulance didn’t arrive in time, well he’d have enjoyed a beer and the great outdoors. Keeping calm gave the ambulance time to save his life, and enough time to finish his beer.
This article covers how Aussies survive snakebites in more detail.
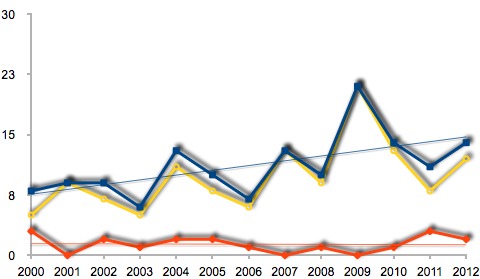
7 and 6) Sharks and Bees
One is the undisputed apex predator of the World’s oceans, the other likes to give people sweet treats. With 16 deaths each, we see the humble honeybee kill as many people as the desperately-in-need-of-a-hug sharks.
I’m sure if we included the deaths from heart disease that bees contribute to with their delicious honey, the bees would rank ahead of the toothy grinned sharks. Even without the heart disease aspect, if we talk long-term averages, honeybees are actually more deadly than sharks in Australia. Bees kill roughly 2 people per year, whilst sharks are only averaging 1 per year.
In the meantime humans are doing their best to wipe out both animals. Sharks are edible, so we kill 100 million of them a year. Colony Collapse Disorder is pretty much a fancy way of saying we are stressing the bees with viruses, diseases, pests, bad food, frequent travel and pesticides, leading to a decline in honey bee numbers.
5) Kangaroo
Stamping its place as the modern day T-Rex, if T-Rexes were vegetarian and spent most of their lives sleeping under a tree, is the kangaroo. With 18 deaths to its name, the kangaroo is getting back at Australians for their love of eating this national icon.
Kangaroos may look loveable and cuddly, but underneath that skin – which is ideal for leather shoes – lays a nasty, vicious bully:
Attacks aren’t that common, but they are hilarious to watch.
The real danger to Aussies from kangaroos is on the roads. Roos are fond of hanging out in the middle of traffic, or leaping out in front of passing cars, so much so that they contribute to 5.5% of road deaths. Not to be outdone, Aussies install Roo-Bars to the front of their vehicles to ensure anything they hit – Roos, pedestrians, children – die instantly.
4) Dogs
Australians love their dogs; they even make movies about them and have landmarks devoted to them. One town is famous for its pet cemetery devoted to dogs. But with 27 deaths to their names, Aussie dogs just don’t seem to love their owners back.
In fairness, dogs are doing Aussies a favour, as they tend to kill kids and old people. The family pet is clearly trying to trim down the weaker members of the pack to make the household stronger, as 78% of attacks are by the pet dog. Legislation is trying to weed out the more suspicious looking dogs, but most dog bites are more a result of the owners than of the dog’s breeding or temperament.
3) Cows
Right now you’re about to say, “Is it really true that all Aussie men are as good looking at Hugh Jackman?” Why yes, it is true. But that is off topic. If you were on topic you’d probably be questioning how cows made this list at all. Are they even Australian? And these things aren’t deadly; they are hamburger fillings and animals that make the green stuff on your dinner plate palatable. Yet cows still managed to kill off 33 Aussies and come in as the third deadliest animal in Australia.
It isn’t like cows have guns in Australia, so how can they be the second most deadly animals? Well, much like kangaroos, cows love to spend time hanging out in the middle of roads, probably deciding which side has greener grass, or looking to hitch a ride to the city. And because Aussies love a good steak, there are more cattle in Australia than people, 26.5 million at last count. That’s a lot of cows trying to hitchhike. Cows also happen to be a fair bit larger than the average kangaroo, so Aussie drivers either die crashing into them, or from crashing into a tree when swerving to avoid them.
The other Aussies on the top of the cow’s hit-list is their chief persecutors: farm workers. Being the biggest of farm animals they account for the majority of animal related deaths on farms, usually by crushing people, or at least their limbs.
2) Horses
That’s right, horses! Just let that fact sink in for a moment. Horses have killed 77 people in a decade in Australia. Australia has sharks, crocodiles, snakes, and spiders that are deadly enough to make Rambo look like a cub scout, but horses killed more people than all of those terrifying critters combined.
So how did horses beat out such deadly competition? Well, 92% of those deaths are from horses deciding they’ve had enough of someone sitting on their back. The rest of the time the horses decide that they need to crush or trample people, possibly to see if humans can be made into glue as well.
1) Humans
Was this ever in doubt? Humans are by far the most deadly Aussie animals. When you compare the animal deaths to other causes of death in Australia, like drowning killing 290 per year, or car accidents killing 1200 people per year, it is clear that even the most deadly of Aussie creatures, the horse, just aren’t that deadly.
But Aussies are generally getting better at not killing each other. There are 270 murders per year and this rate has been declining for the past 20 years. If this trend continues, then within a decade all the other animals in Australia may actually kill more Aussies than people murdering each other.
In the meantime, if you want to stay safe in Australia: don’t let a horse drive your car near water while you argue with an Aussie about whether that’s a knife. Safety first.
Update: Okay, so this piece is a few years old now and more recent data is available from a ANHMRC study looking at data from 2000-2013.
| Creature | Deaths (2000-2013) |
Hospitalisations (2001-2013) |
|---|---|---|
| Snakes | 27 | 6,123 |
| Hornets, wasps and bees | 25 bees, 2 wasps | 12,351 |
| Spiders | 0 | 11,994 |
| Ticks and ants | 5 | 4,533 |
| Marine animals | 3 | 3,707 |
| Scorpions | 0 | 61 |
| Centipedes / millipedes | 0 | 119 |
| Unknown animal or plant | 2 | 536 |
Since 2000, 74 people have died from being thrown or trampled by a horse. Twenty-six people have died from shark attack and 23 from altercations with dogs. Crocodiles have been responsible for 19 deaths.
And compared to 4,820 drowning deaths and 974 deaths from burns in the same period, the snake bite figures figures are still remarkably low. (Source)
Horses and humans still on top!!